ROS与STM32通信(一)-rosserial
硬件
- STM32F103c8t6
- OLED(I2C)
- USB2TTL
- Stlink
接线
OLED(GPIO模拟I2C)
| 硬件 |
引脚 |
| OLEDSCL |
PA4 |
| OLEDSDA |
PA5 |
USART1
| 硬件 |
引脚 |
作用 |
| RX |
PA9 |
USART1_TX |
| TX |
PA10 |
USART1_RX |
LED
| 硬件 |
引脚 |
| LED0 |
PC13 |
| LED1 |
PC15 |
软件
STM32CubeMX配置
- SYS->Debug->Serial Wire
- RCC->HSE->Crystal/Ceramic Resonator
- PC15->OutPut ,Label为LED0
- PC13->OutPut ,Label为LED1
- TIM1->Clock Source->Internal Clock
- 时钟树,时钟设置为72M
- USART1->Asynchronous Baud Rate: 115200
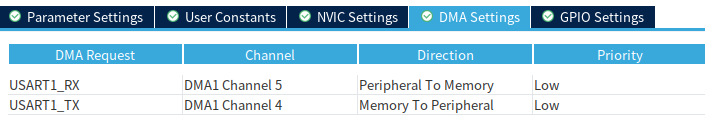
设置DMA
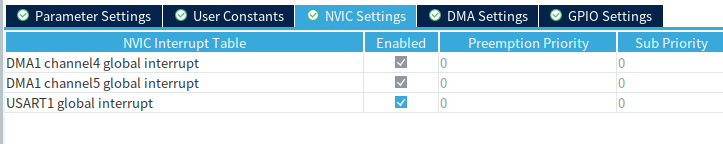
开启串口中断
rosserial
rosserial是ROS中的一个重要模块,它实现了ROS通信协议与各类嵌入式硬件平台之间的桥接,大大简化了ROS在底层硬件上的移植和应用。rosserial通过消息序列化和常用串行通信接口,实现了ROS主机和嵌入式客户端之间的消息交互,为各种嵌入式平台提供了C++和Python的ROS客户端库,使得在这些硬件上也能方便地使用ROS的通信架构来进行节点管理、话题通信和服务调用。rosserial还支持动态主题和服务,以较小的代码占用实现ROS功能,具有很强的可移植性。因此,rosserial是ROS物联网和机器人应用不可或缺的重要组件,极大地便利了ROS在各类嵌入式系统和小型机器人产品上的移植应用和开发。
rosserial_WIKI

rosserial_stm32 Github地址
本文资源包stm32f103c8t6_rosserial, CSDN资源下载
移植
下载上述资源stm32f103c8t6_rosserial
1
| git clone https://github.com/GHigher12/STM32f103c8t6_rosserial.git
|
or 直接在CSDN下载
将RosLibs文件夹添加到stm32工作文件里

还有Core文件夹中的mainpp.h , round.h, mainpp.cpp
此时如果用Clion作为开发环境还需要修改CMakeList.txt
包含文件的路径

main.c使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
#include "mainpp.h"
int main(void)
{
setup();
while (1)
{
loop();
}
}
|
上位机订阅-下位机发布
上位机订阅
python订阅 demo01_sub_py.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import String
if __name__ == "__main__":
rospy.init_node("ros_pc_pub")
pub = rospy.Publisher("pc_to_stm32",String,queue_size=10)
msg = String()
msg_front = "ros_2_stm32->"
count = 0
rate = rospy.Rate(1)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
msg.data = msg_front + str(count)
pub.publish(msg)
rate.sleep()
rospy.loginfo("发布的数据为:%s",msg.data)
count += 1
|
c++订阅 demo01_sub_c.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| #include "ros/ros.h"
#include "std_msgs/String.h"
#include <sstream>
void doMsg(const std_msgs::String::ConstPtr &msg)
{
ROS_INFO("订阅的数据为: %s", msg->data.c_str());
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
ros::init(argc, argv, "ros_pc_sub");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Subscriber sub = nh.subscribe("stm32_to_pc", 10, doMsg);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
|
安装rosserial_python
1
| sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-rosserial-python
|
下位机发布
mainpp.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| #include <mainpp.h>
#include <ros.h>
#include <std_msgs/String.h>
#include "main.h"
ros::NodeHandle nh;
std_msgs::String stm32_to_pc_word;
ros::Publisher stm32_to_pc("stm32_to_pc", &stm32_to_pc_word);
void HAL_UART_TxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart){
nh.getHardware()->flush();
}
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart){
nh.getHardware()->reset_rbuf();
}
char hello[13] = "hello ros!";
u8 cnt = 0;
void setup(void)
{
nh.initNode();
nh.advertise(stm32_to_pc);
}
void loop(void)
{
cnt+=1;
sprintf(oledBuf,"stm32_2_ros->%d",cnt);
OLED_ShowString(0,24,(u8*)oledBuf,16);
OLED_Refresh();
stm32_to_pc_word.data = oledBuf;
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(LED0_GPIO_Port, LED0_Pin);
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(LED1_GPIO_Port, LED1_Pin);
HAL_Delay(1000);
stm32_to_pc.publish(&stm32_to_pc_word);
nh.spinOnce();
}
|
编译将程序烧录到stm32中
通信
将usb2ttl连接好usart1,连接电脑
执行下列命令
1
2
3
| lsusb
ls /dev/ttyUSB*
sudo chmod 777 /dev/ttyUSB0
|
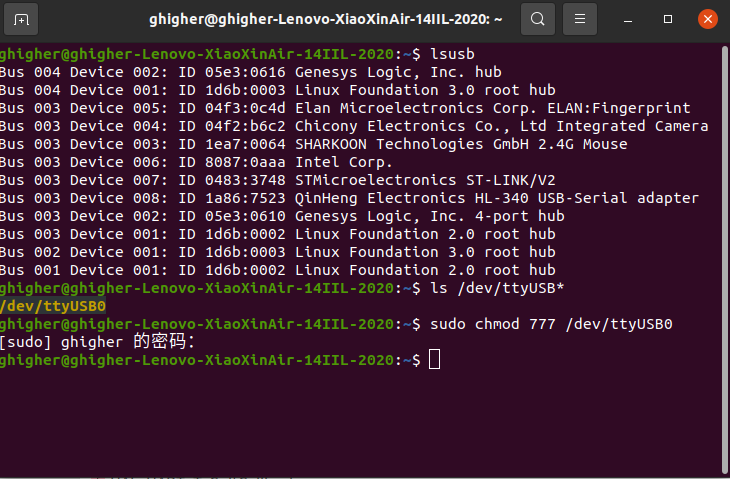
启动rosserial_python节点
1
2
| roscore
rosrun rosserial_python serial_node.py _port:=/dev/ttyUSB0 _baud:=115200
|
出现以下内容则表示运行正常
1
2
3
4
5
| [INFO] [1690446448.903399]: ROS Serial Python Node
[INFO] [1690446448.908570]: Connecting to /dev/ttyUSB0 at 115200 baud
[INFO] [1690446451.013146]: Requesting topics...
[INFO] [1690446451.772474]: Note: publish buffer size is 512 bytes
[INFO] [1690446451.774498]: Setup publisher on stm32_to_pc [std_msgs/String]
|
可使用rostopic echo /stm32_to_pc查看话题
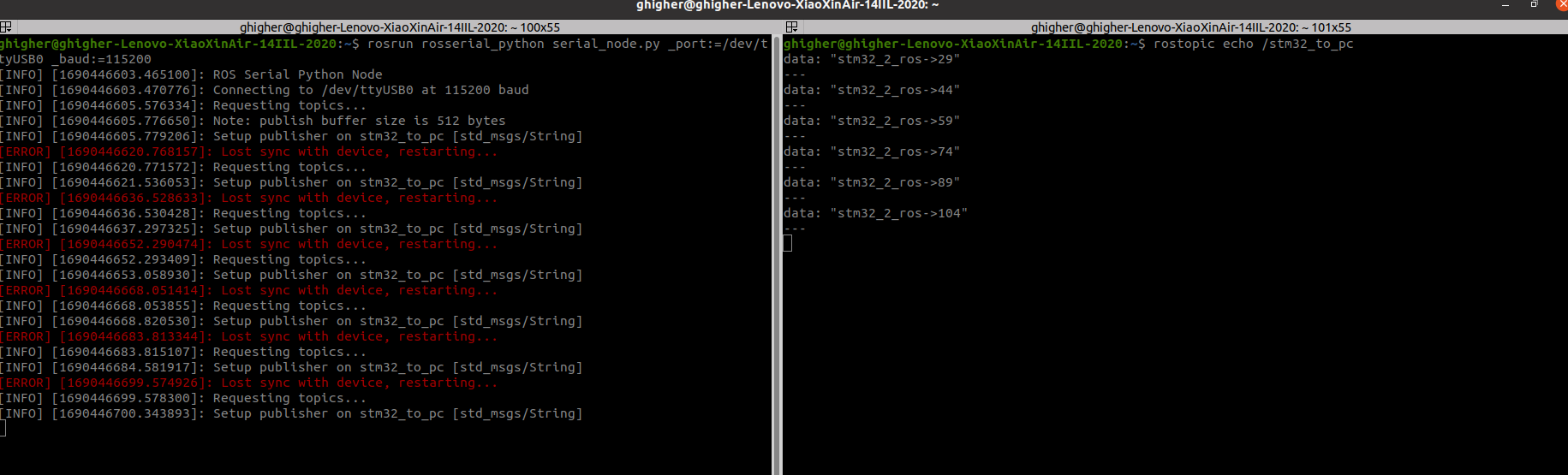
不过这里会出现[ERROR] [1690446652.290474]: Lost sync with device, restarting...报错,导致收发频率不一致,博主现在还没解决,如有读者有解决办法,可在评论留言。
python订阅
1
2
3
| cd ~/catkin_ws
source ./devel/setup.bash
rosrun hello_vscode demo01_sub_py.py
|
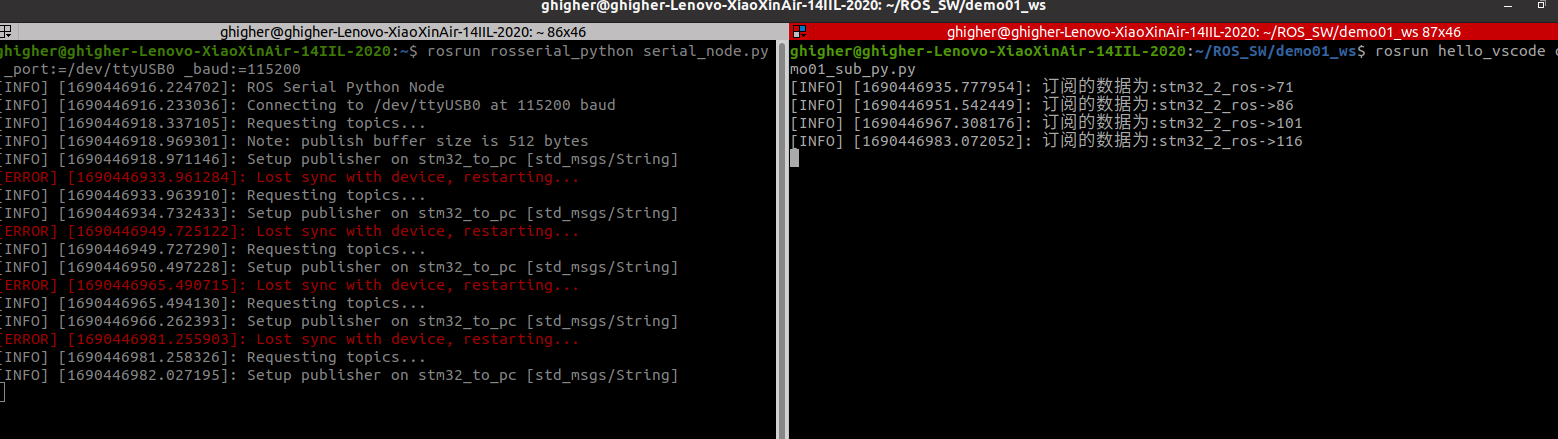
c++订阅
1
2
3
| cd ~/catkin_ws
source ./devel/setup.bash
rosrun hello_vscode demo01_sub_c
|
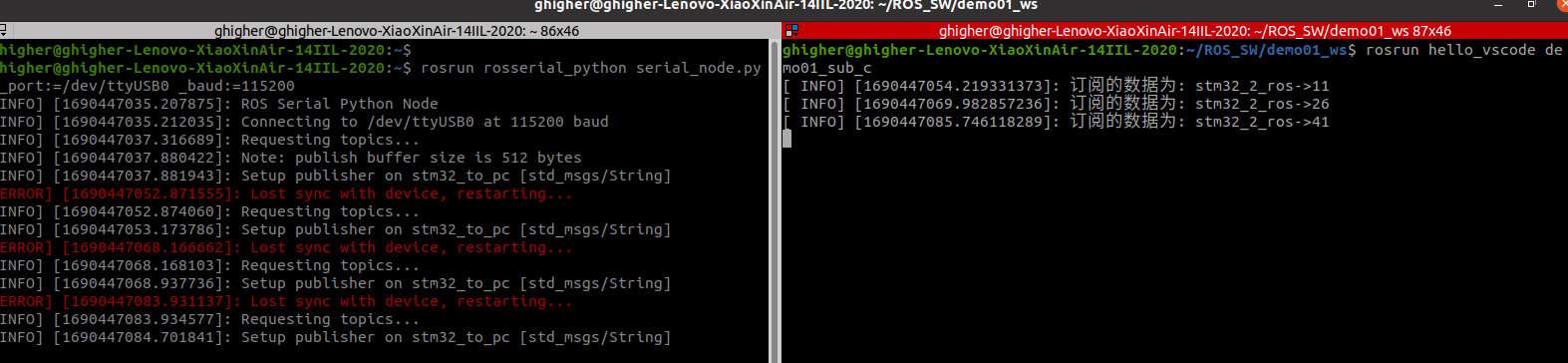
下位机显示

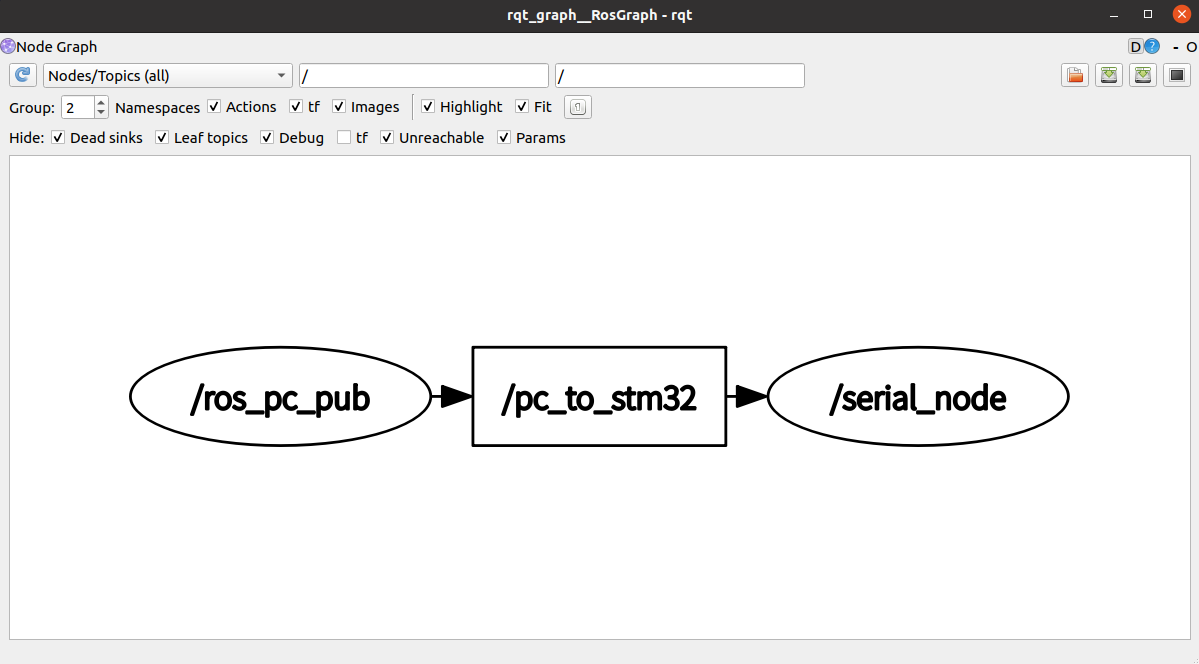
查看rqt_graph
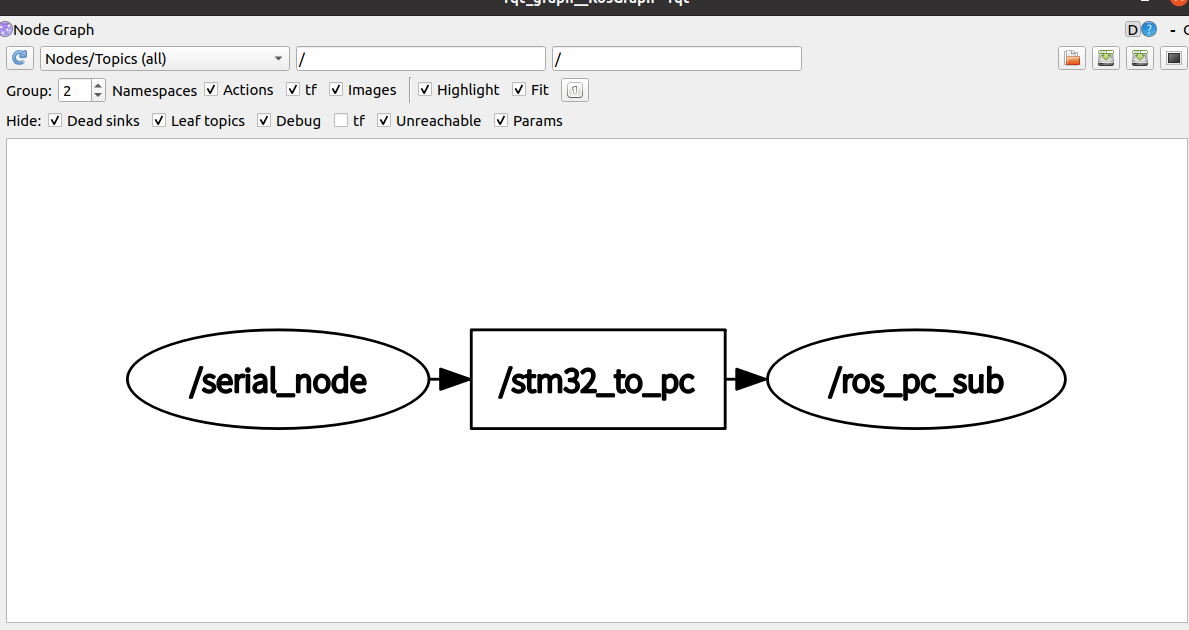
上位机发布-下位机订阅
上位机发布
python发布 demo01_pub_py.py
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import String
if __name__ == "__main__":
rospy.init_node("ros_pc_pub")
pub = rospy.Publisher("pc_to_stm32",String,queue_size=10)
msg = String()
msg_front = "ros_2_stm32->"
count = 0
rate = rospy.Rate(1)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
msg.data = msg_front + str(count)
pub.publish(msg)
rate.sleep()
rospy.loginfo("发布的数据为:%s",msg.data)
count += 1
|
c++发布 demo01_pub_c.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| #include "ros/ros.h"
#include "std_msgs/String.h"
#include <sstream>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
ros::init(argc, argv, "ros_pc_pub");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::Publisher pub = nh.advertise<std_msgs::String>("pc_to_stm32", 10);
std_msgs::String msg;
ros::Rate rate(1);
int count = 0;
ros::Duration(3).sleep();
while (ros::ok)
{
count++;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "ros_2_stm32->" << count;
msg.data = ss.str();
pub.publish(msg);
ROS_INFO("发布的数据为: %s", ss.str().c_str());
rate.sleep();
ros::spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
|
下位机订阅
mainpp.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| #include <mainpp.h>
#include <ros.h>
#include <std_msgs/String.h>
#include "main.h"
void command_callback( const std_msgs::String& rxbuff);
ros::NodeHandle nh;
std_msgs::String stm32_to_pc_word;
ros::Subscriber<std_msgs::String> cmd_sub("pc_to_stm32", command_callback);
void command_callback(const std_msgs::String &rxbuff)
{
char oled_rxbuff[128];
stm32_to_pc_word = rxbuff;
snprintf(oled_rxbuff, sizeof(oled_rxbuff), "%s", rxbuff.data);
OLED_ShowString(0,24, (u8*)oled_rxbuff,16);
OLED_Refresh();
}
void HAL_UART_TxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart){
nh.getHardware()->flush();
}
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart){
nh.getHardware()->reset_rbuf();
}
void setup(void)
{
nh.initNode();
nh.subscribe(cmd_sub);
}
void loop(void)
{
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(LED0_GPIO_Port, LED0_Pin);
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(LED1_GPIO_Port, LED1_Pin);
HAL_Delay(1000);
nh.spinOnce();
}
|
通信
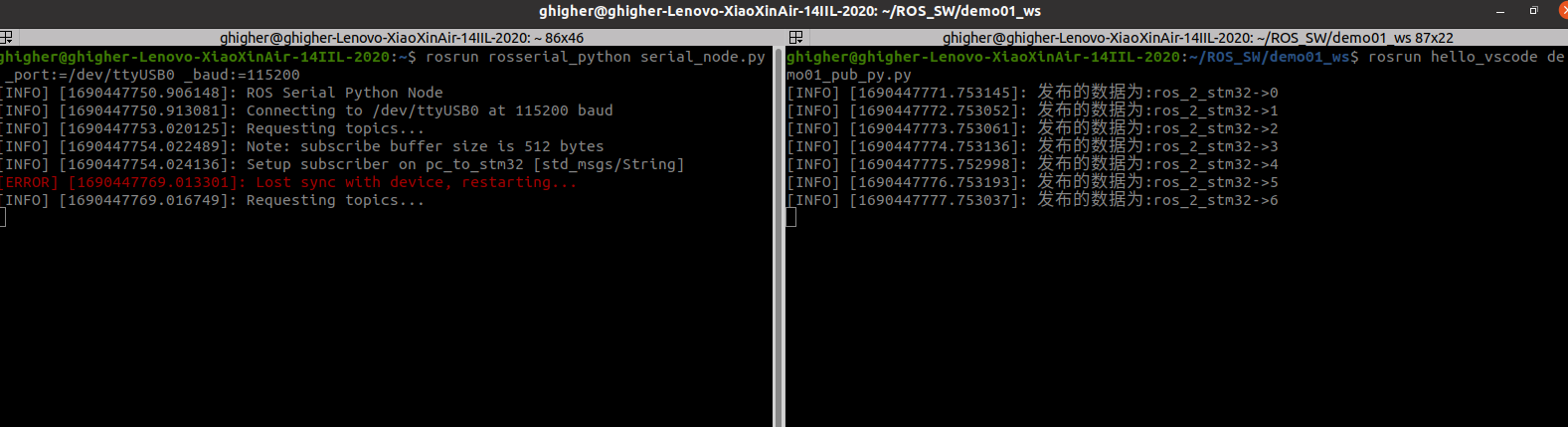
python发布
1
| rosrun hello_vscode demo01_pub_py.py
|
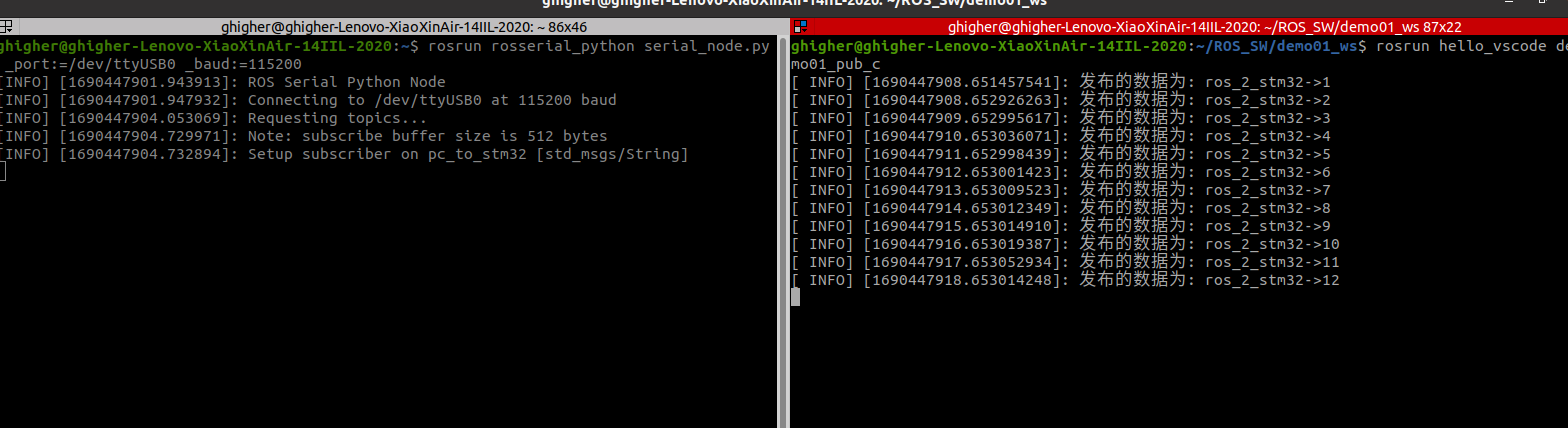
c++发布
1
| rosrun hello_vscode demo01_pub_c
|
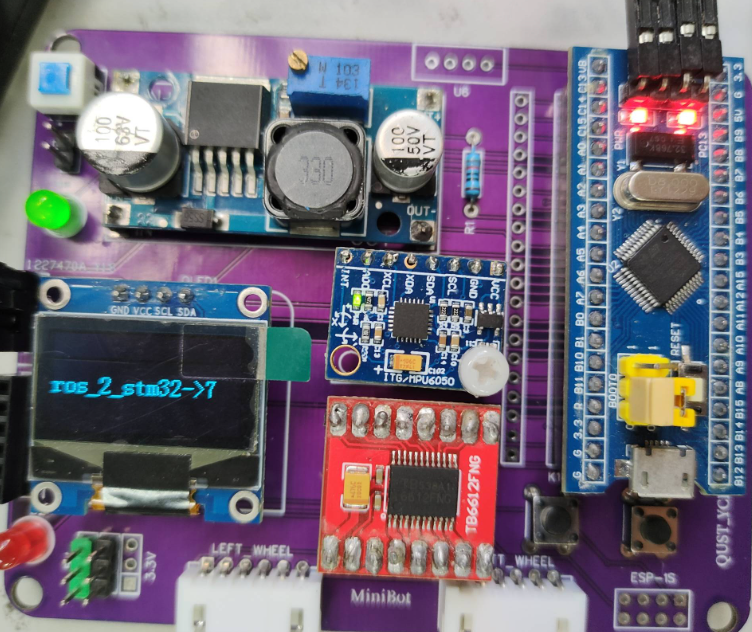
下位机显示
查看rqt_graph